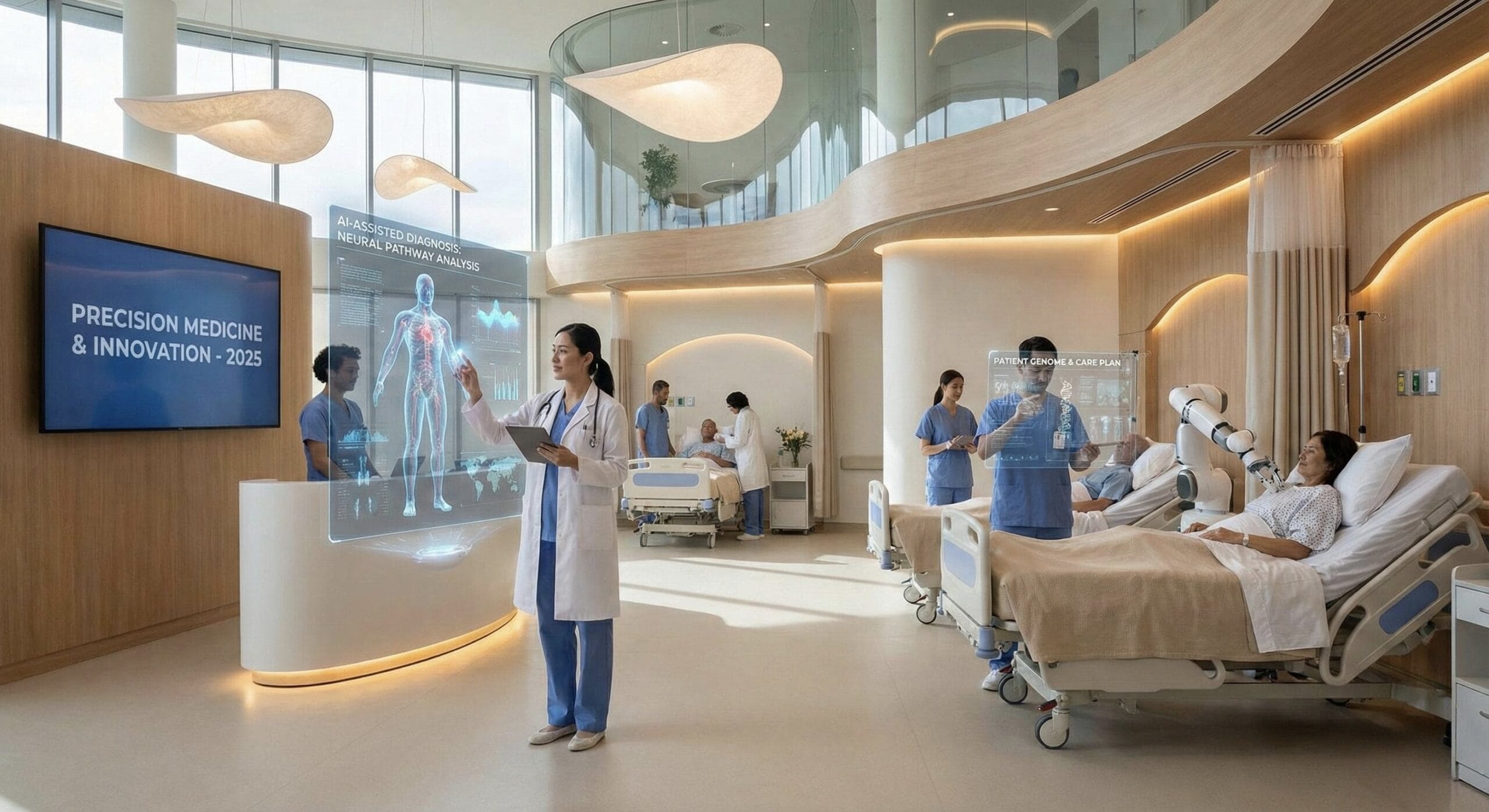
A System Under Pressure and Transformation
The second half of 2025 represents a decisive turning point for global healthcare. Systems that once experimented with digital tools are now demanding measurable returns. At the same time, biological science is advancing rapidly, reshaping therapy development. Yet, workforce shortages, financial strain, and widening care deserts threaten core access. These opposing forces define the new landscape.
AI Shifts From Experimentation to Real ROI
Providers now treat artificial intelligence as essential infrastructure. Large health systems, facing severe staffing and margin pressures, lead adoption. Smaller practices and most payers continue to lag. As a result, AI spending surged in 2025 and is heavily concentrated among hospitals.
Ambient Intelligence Becomes a Workforce Tool
Ambient clinical documentation has become the standout use case. These systems listen to clinician–patient conversations and generate structured notes automatically. Because of this, clinicians gain back one to two hours daily. Reduced after-hours charting also improves retention, making ambient AI a stabilizing force.
Revenue Integrity Automation Strengthens Financial Health
AI-driven coding and billing tools now reduce denial rates and speed reimbursement. Given rising costs and flat revenue, these tools serve as financial lifelines. Prior authorization automation is also reshaping payer provider friction by shortening approval delays.
Next Phase: Autonomous Clinical Agents
The industry is moving beyond copilots. Autonomous clinical agents can triage, schedule follow-ups, and reconcile medications without constant prompting. Likewise, multimodal AI combines genomics, imaging, EHR notes, and wearable data into unified insights. This shift supports more precise diagnostics and more consistent care.
Generative AI Accelerates Drug Discovery
Life sciences organizations are using generative AI to compress drug development timelines. Companies are simulating molecular interactions, predicting protein structures, and identifying biomarkers in silico. This reduces early-stage failures and speeds candidate selection.
Advanced modeling is also guiding CRISPR experiments. In 2025, integrated AI-CRISPR approaches improved gene-editing accuracy and safety. These tools are expected to reduce clinical trial risks and expand therapeutic pipelines through 2026.
Breakthroughs in Precision Medicine
Neurology Advances Show Meaningful Benefit
New treatments for agitation in Alzheimer’s disease and for autoimmune neuromuscular disorders showed strong results. For example, AXS-05 greatly reduced agitation relapse without the sedation common in older drugs. In addition, telitacicept delivered significant improvement for myasthenia gravis by targeting the biological roots of autoantibody production.
Cardiology and Gene Therapy Enter “One-and-Done” Era
CRISPR-based therapies targeting cholesterol regulation demonstrated lasting lipid reductions after a single intervention. Gene therapy for sickle cell disease continued to show systemic benefits, including improved cerebral blood flow. Meanwhile, simpler pharmacologic innovations—like triple-combination hypertension pills—are improving adherence and outcomes at scale.
A Deepening Workforce Crisis
Shortages Across All Disciplines
By late 2025, global and U.S. healthcare systems faced severe worker shortages. Nearly all physician specialties reported supply deficits. Direct care roles, including home health aides, suffered high turnover due to low wages and difficult working conditions. As a result, access to essential care remains strained.
Burnout and Labor Activism Intensify
Widespread burnout has led to a rise in labor activism. Large strikes in U.S. health systems and internationally highlight demands for safe staffing, not just higher pay. Many clinicians argue that existing operating models are unsafe and unsustainable. These actions signal deep systemic fatigue.
Technology Supports a Hybrid Workforce
Health systems are adopting virtual nursing, AI-enabled scheduling, and robotic process automation. These tools relieve administrative burden and let clinicians focus on high-value tasks. Hybrid models where digital tools extend human reach are emerging as the new norm.
Rural Hospital Closures and the Access Crisis
Rural America faces severe declines in access. Labor and delivery closures continue at alarming rates, creating maternity deserts. Women often travel more than 50 minutes for care, raising risks for complications. Financial pressure drives most closures, as rural hospitals struggle with persistent losses. Without policy intervention, these trends will accelerate.
Care Delivery Shifts Toward Home and Virtual Models
Telehealth Becomes Integrated Care
Telehealth in 2025 has matured from video visits to fully integrated chronic-care management. Remote monitoring and AI-driven wearables detect early risk signals, enabling preventive outreach. Consequently, clinicians can intervene before conditions escalate.
Virtual Wards Expand Capacity
Hospital-at-home programs continue to grow. These models support moderate- and high-acuity patients at home using connected devices, analytics, and remote clinical teams. When properly staffed, virtual wards reduce bed strain and costs.
Behavioral Health Integration Gains Momentum
Collaborative care and primary care behavioral health models are expanding. Primary care teams now work closely with behavioral health managers and psychiatric consultants. This reduces wait times and improves continuity. CMS’s Innovation in Behavioral Health (IBH) model further supports integrated care, especially for Medicaid and Medicare beneficiaries.
Policy Shifts: Food as Medicine and Value-Based Care
Nutrition Enters the Clinical Mainstream
Food as Medicine (FaM) formally entered the policy arena in 2025. Federal initiatives and Medicaid waivers are supporting medically tailored meals and produce prescriptions. Since diet-related diseases cost the U.S. over $1 trillion annually, FaM offers a cost-effective complement to pharmaceutical interventions, including GLP-1 drugs.
Economic Pressure Accelerates Value-Based Care
Inflation, high labor expenses, and flat reimbursement continue to strain hospital finances. Consequently, systems are accelerating their transition into value-based care. These models reward prevention and coordinated care, but they also require major infrastructure investments—challenging for small and rural hospitals.
Looking Toward 2026: Interoperability, Digital Twins, and Companionship AI
The next phase of healthcare transformation hinges on strategic interoperability. Unified data platforms will enable safe, cross-system AI agents and multimodal insights. Digital twins may allow simulations of personalized treatment responses before any real exposure.
Additionally, loneliness is emerging as a global health risk. AI-driven companionship tools for older adults may help reduce isolation, detect early cognitive decline, and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion: A System Balancing Crisis and Capability
Healthcare in late 2025 is defined by dual forces. On one side, workforce shortages, rural closures, and economic pressures threaten stability. On the other, breakthroughs in AI, precision medicine, and nutrition policy offer unprecedented tools for improvement.
Success in 2026 and beyond will depend on organizations that redesign workflows around technology, invest in their people, and embrace prevention alongside treatment. The future system must be both high-tech and high-touch using digital tools to strengthen the human connection at the heart of care.